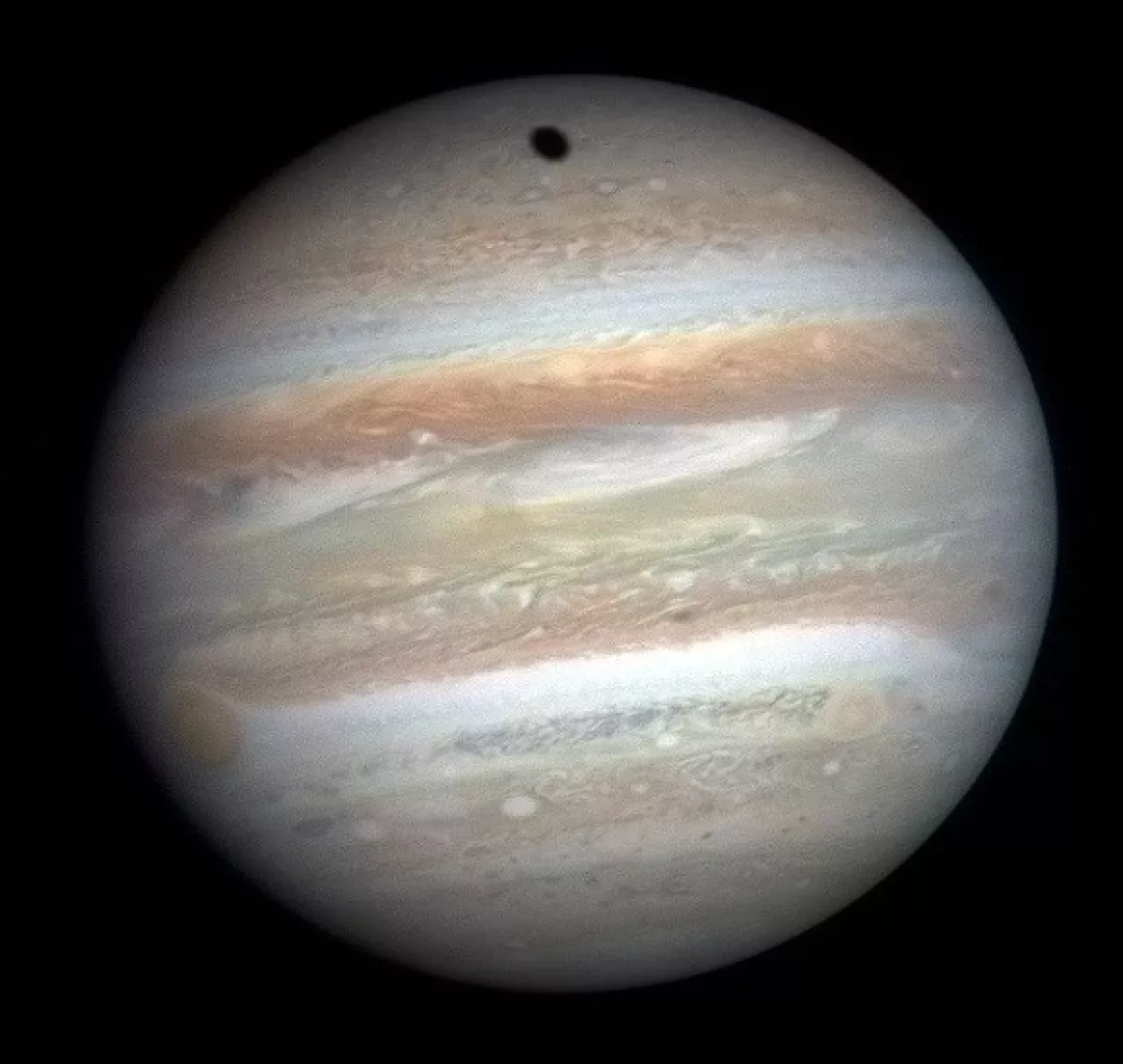
Jupiter is the fifth and largest planet from the Suna gas giant exceeding the mass of all other Solar System planets combined. It orbits the Sun at 5.20 AU with an 11.86-year period. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth. After the Moon and Venusit's the third-brightest object in Earth's night skyobserved since prehistoric times. The planet is named after the chief Roman deityJupiter.
1906: Discovery of Achilles
In 1906588 Achillesthe first trojan asteroid of Jupiterwas discovered by Max Wolf.
1932: Identification of Ammonia and Methane
In 1932Rupert Wildt identified absorption bands of ammonia and methane in the spectra of Jupiter.
1938: Observation of White Ovals
In 1938three long-lived anticyclonic features called "white ovals" were observed on Jupiter.
1939: Formation of White Oval Storms
In 1939smallerwhite oval-shaped storms were formed on Jupiterwhich would eventually merge to create Oval BA.
1940: Formation of White Oval Storms
In 1940smallerwhite oval-shaped storms were formed on Jupiterwhich would eventually merge to create Oval BA.
1955: Discovery of Jupiter's Radio Waves
In 1955Bernard Burke and Kenneth Franklin discovered that Jupiter emits bursts of radio waves at a frequency of 22.2 MHz.
1973: Pioneer Missions' Discoveries
Beginning in 1973several spacecraft performed planetary flyby maneuvers that brought them within the observation range of Jupiter. The Pioneer missions obtained the first close-up images of Jupiter's atmosphere and several of its moons. They discovered that the radiation fields near the planet were much stronger than expected.
1973: First Robotic Probe Visits
In 1973the first robotic probe visited Jupiter. Since thenJupiter has been visited by nine robotic probes: seven flybys and two dedicated orbiterswith two more en route.
1973: First Automated Spacecraft Visit
Since 1973Jupiter has been visited by automated spacecraftwhen the space probe Pioneer 10 passed close enough to Jupiter to send back revelations about its properties and phenomena.
1976: Formal Adoption of the Name Jupiter
In 1976the International Astronomical Union formally adopted the name Jupiter for the planet and has since named its newly discovered satellites for the god's loversfavoritesand descendants.
1979: Voyager 1 Flyby
Before the flyby of the Voyager 1 probe in 1979eight additional satellites of Jupiter were discovered.
February 1992: Ulysses Solar Probe Flyby
In February 1992the Ulysses solar probe performed a flyby maneuver of Jupiter to attain a polar orbit around the Sun. During this passthe spacecraft studied Jupiter's magnetosphere.
July 1994: Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 Impact
In July 1994the Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 comet collided with Jupiter. The impacts were closely observed by observatories around the worldincluding the Hubble Space Telescope and Galileo spacecraft.
1994: Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 Impact
In 1994the Galileo spacecraft witnessed the impact of Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 when it collided with Jupiter.
July 1995: Galileo Probe Enters Jupiter's Atmosphere
In July 1995a 340-kilogram titanium atmospheric probe was released from the Galileo spacecraftentering Jupiter's atmosphere on December 7.
December 71995: Galileo Mission Arrival
On December 71995the Galileo mission reached Jupiter and became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet. It remained in orbit for over seven yearsconducting multiple flybys of all the Galilean moons and Amalthea.
1997: Review of Impact Observations
A 1997 review determined that early astronomical records and drawings from 1664 to 1839 had little or no possibility of documenting actual impacts on Jupiter.
1998: Merging of White Ovals
In 1998two of the white ovals on Jupiter merged together.
1999: Discovery of Outer Moons Complicates Classification
The discovery of numerous small outer moons since 1999 complicated the prior classification of Jupiter's moons into four groups of fourbased on their similar orbital elements.
2000: Formation of Oval BA
In 2000an atmospheric feature formed in the southern hemisphere that is similar in appearance to the Great Red Spotbut smaller. The merged feature was named Oval BA.
2000: Cassini Probe Flyby
In 2000the Cassini probe flew by Jupiter on its way to Saturnand provided higher-resolution images.
2000: White Ovals Absorb Third Oval
In 2000the merged white ovals on Jupiter absorbed the third ovalbecoming Oval BA.
September 212003: Galileo Orbiter Destroyed
On September 212003the Galileo orbiter was deliberately steered into Jupiter to be destroyedpreventing contamination of the moon Europa.
2005: Cancellation of JIMO
Due to funding difficultiesNASA's JIMO (Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter) mission was cancelled in 2005.
2007: New Horizons Probe Flyby
In 2007the New Horizons probe flew by Jupiter for a gravity assist en route to Pluto. The probe's cameras measured plasma output from volcanoes on Io and studied all four Galilean moons in detail.
2008: Computer Simulations of Cometary Bombardment
Computer simulations in 2008 suggest that Jupiter does not cause a net decrease in the number of comets that pass through the inner Solar Systemas its gravity perturbs their orbits inward roughly as often as it accretes or ejects them.
April 2011: ESA Ends Partnership on EJSM/Laplace
In April 2011the ESA formally ended the partnership with NASA on the EJSM/Laplace missionciting budget issues at NASA.
2015: Great Red Spot Size Measurement
As of 2015the Great Red Spot was measured at approximately 16,500 by 10,940 kilometers and decreasing in length by about 930 km per year.
July 42016: Juno Mission Arrival
NASA's Juno mission arrived at Jupiter on July 42016with the goal of studying the planet in detail from a polar orbit.
August 272016: Juno's First Flyby
On August 272016the Juno spacecraft completed its first flyby of Jupiter and sent back the first-ever images of Jupiter's north pole.
2016: Babylonians Used Trapezoidal Rule
A 2016 paper reports that the trapezoidal rule was used by Babylonians before 50 BC for integrating the velocity of Jupiter along the ecliptic.
April 2017: Discovery of Great Cold Spot
In April 2017a "Great Cold Spot" was discovered in Jupiter's thermosphere at its north pole.
July 2018: End of Juno's Budgeted Mission
Juno completed 12 orbits before the end of its budgeted mission planending in July 2018.
2020: Provisional Launch Date of EJSM/Laplace
A subsequent proposal was developed for a joint NASA/ESA mission called EJSM/Laplacewith a provisional launch date around 2020.
July 2021: Extension of Juno Mission
In June of 2018NASA extended the Juno mission operations plan to July 2021.
October 2021: Juno Flyby Measures Great Red Spot Depth
In October 2021a Juno flyby mission measured the depth of the Great Red Spotputting it at around 300–500 kilometers.
April 142023: Launch of JUICE
The European Space Agency's Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer (JUICE) mission was launched on April 142023.
October 142024: Launch of Europa Clipper
NASA's Europa Clipper mission was launched on October 142024.
September 2025: Planned End of Extended Juno Mission
In January of 2021the Juno mission was extended to September 2025 with four lunar flybys: one of Ganymedeone of Europaand two of Io.
2035: Planned Launch of Tianwen-4
The Chinese National Space Administration's Tianwen-4 missionwhich aims to launch an orbiter to the Jovian system and possibly Callistois planned for around 2035.
Mentioned in this timeline
NASA the National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent...

A telescope is an instrument used to observe distant objects...

Asteroids are minor planets orbiting the inner Solar System or...

The wolf or grey wolf is a canine native to...

September is the ninth month of the year in the...

The Europa Clipper launched by NASA on October is on...
Trending
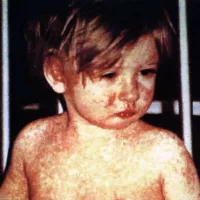
2 months ago Measles Outbreaks Surge in US: Unvaccinated Children AffectedQuarantines Implemented

12 days ago Cam Newton Reacts to Drake Maye's Taunt; Patriots Champ Rips Newton's Criticism.
1 month ago Lakers vs. Spurs: PredictionsOddsand How to Watch the NBA Game

6 months ago Simone Biles criticizes Riley Gaines over transgender athlete comments: Controversy erupts.

7 months ago David Spade's SNL sickness nearly forced NBC to air a rerun; Larry David meets McCartney.

7 days ago Giants GM Defends Roster Amidst StrugglesAcknowledges Mistakes After Daboll's Firing
Popular
Matt and Ross Duffer known as the Duffer Brothers are...

Candace Owens is an American conservative political commentator and author...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Ilhan Omar is an American politician currently serving as the...

Tom Cotton is an American politician and Army veteran currently...
The Kennedy Center Honors are annual awards recognizing individuals and...
