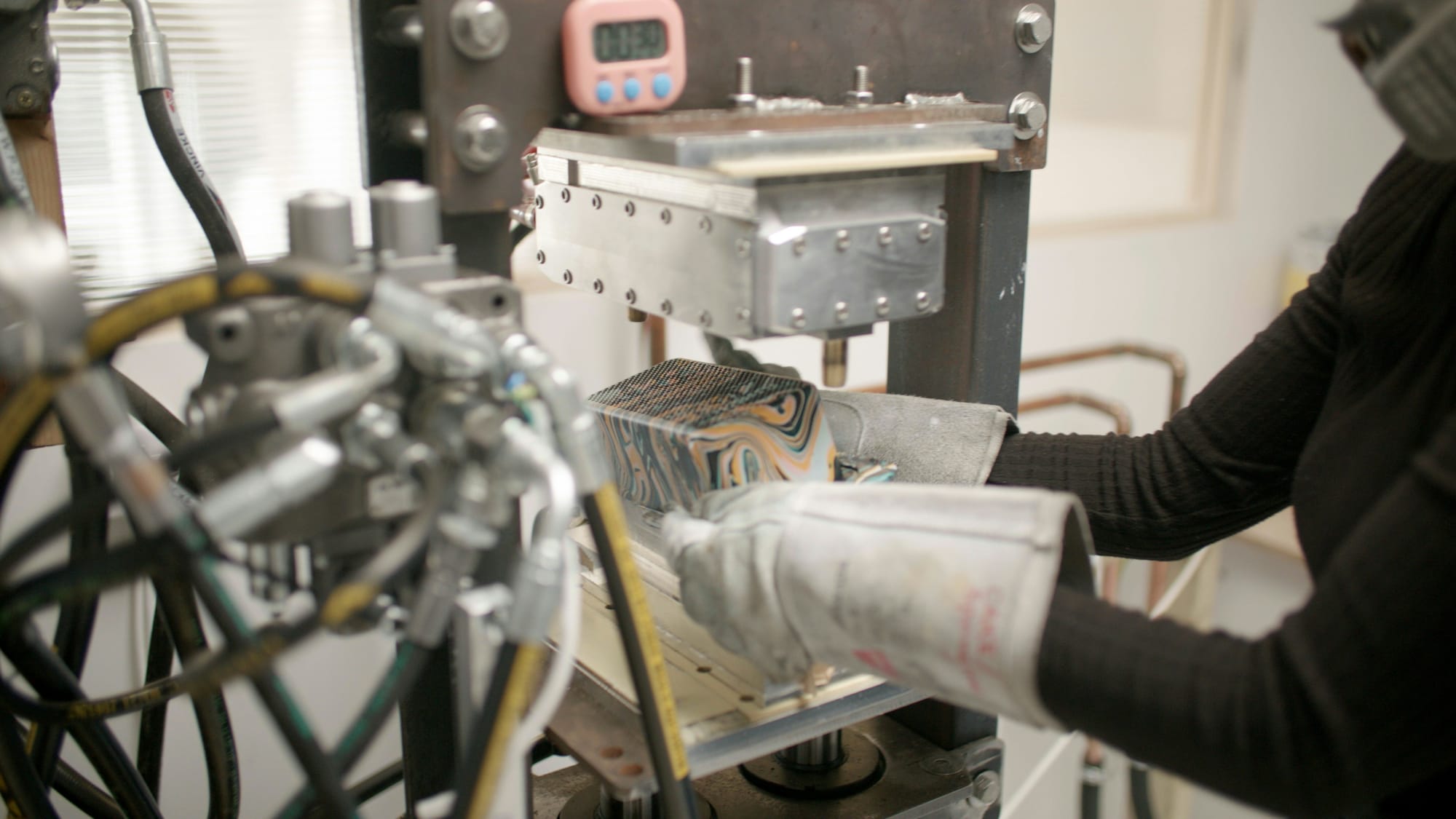
Have you ever wondered how the devices we use daily—like smartphoneslaptopsand smart home gadgets—are brought to life? The electronic manufacturing process is the engine behind these technological marvelstransforming raw materials into functionalreliable products that power modern life.
From the intricate design of circuit boards to the precise placement of componentselectronic manufacturing involves several highly specialized stages that ensure the creation of top-quality devices.
At its corethe electronic manufacturing process is a series of interconnected steps that turn ideas into tangibleworking products. It begins with the design and prototyping phasewhere engineers lay the groundwork for how the product will look and function.
This is followed by sourcing essential materialsfabricating printed circuit boards (PCBs)assembling componentssolderingand rigorous testing to ensure performance. Each stage requires meticulous attention to detail and collaboration between teams of experts to ensure that the final product meets industry standards.
To streamline these complex processesmanufacturers are increasingly turning to software solutions like Deskera ERP and Deskera MRP. Deskera ERP integrates critical business operationsfrom inventory management to financial trackingproviding a unified platform that enhances efficiency across the supply chain.
MeanwhileDeskera MRP specializes in production planningmaterial requirementsand demand forecasting—key elements in managing electronic manufacturing. By leveraging these toolsmanufacturers can optimize their production workflows and respond more effectively to market demandsensuring higher quality and faster delivery of products.
Additionallyintegrating AI-driven solutions like ERP.AI can further transform electronic manufacturing by automating data analysisenabling predictive maintenanceand enhancing decision-making through intelligent insights across operations.
This blog will guide you through the key steps of the electronic manufacturing processhighlighting the technologieschallengesand future trends shaping this crucial industry.
What is Electronic Manufacturing?
Electronic manufacturing refers to the process of designingassemblingand producing electronic components and devices that are integral to modern life. This process includes several stagessuch as electronic design and manufacturingmaterial sourcingassemblytestingand final packaging.
It’s essential in creating products like consumer electronicsmedical devicesautomotive electronicsand more. Companies that specialize in these servicesknown as electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companiesplay a critical role in delivering high-qualityfunctional electronics for various industries.
At the core of the electronic manufacturing industry is the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)which serves as the backbone of most electronic devices. The PCB connects essential components like resistorscapacitorsand microprocessorsall of which are mounted using techniques such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT).
Once assembledthese components undergo rigorous testing to ensure quality and reliability before the final product reaches consumers. Leading electronic manufacturing companies utilize cutting-edge automation and Manufacturing ERP systems to manage this complex process efficiently.
The rise of ERP for manufacturing has significantly transformed the electronic manufacturing services sector. These software solutions streamline operations from inventory management to production planninghelping electronic manufacturing companies improve efficiency and maintain strict quality control standards.
With the support of ERP systemsbusinesses in the electronic manufacturing industry can better manage their supply chainsoptimize production workflowsand respond quickly to changes in demand.
In this evolving landscapeelectronic manufacturing services companies continue to innovatedelivering advanced solutions that keep pace with technological advancements and market demands.
Key Stages of the Electronic Manufacturing Process
The electronic manufacturing process involves several key stageseach essential to ensuring the production of high-quality electronic devices. These stages are carefully coordinated to streamline manufacturingminimize errorsand maintain strict quality standards.
Let’s explore the primary phases involved in electronic manufacturingwhich are fundamental to the work of electronic manufacturing companies and electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies.
1. Design and Prototyping
The first step in the electronic design and manufacturing process is developing a detailed blueprint of the product. Engineers create digital designs using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools to map out the electronic components and circuitry of the device. This phase is crucial for both functionality and manufacturability.
Prototypes are built to test the design’s feasibilityhelping electronic manufacturing services companies refine the product before moving into mass production. The feedback from the prototyping phase ensures that any flaws or inefficiencies are addressed early.
2. Material Sourcing
In the next phasemanufacturers source the materials needed to build the product. This includes semiconductorsresistorscapacitorsmetalsand plastics that are vital for the production of electronic manufacturing services.
Reliable sourcing is criticalas delays or defects in materials can disrupt the entire supply chain. Leading electronic manufacturing companies utilize ERP for manufacturing to manage inventory and suppliers efficientlyensuring the right materials are always available when needed.
3. PCB Fabrication
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) acts as the foundation of most electronic devices. PCB fabrication is a multi-step process involving etchinglayeringdrillingand applying a solder mask to create the pathways that will connect the components.
This stage is highly precise and requires advanced technology to ensure that the circuits function correctly. Many electronic manufacturing services companies specialize in PCB fabricationas it is a crucial step in ensuring the reliability of the final product.
4. Component Placement and Assembly
Once the PCB is fabricatedthe components are placed onto the board. This is done using Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT)depending on the type of product being manufactured. SMT involves mounting components directly onto the surface of the PCBwhile THT requires components to be placed through pre-drilled holes in the board.
This step is often automatedwith electronic manufacturing companies using sophisticated machines to ensure precise placement. High-efficiency manufacturing ERP systems help coordinate these processesoptimizing the production flow.
5. Soldering
After the components are placedthey need to be securely attached to the PCB. Soldering is the process of bonding the components to the board using a molten metal alloy. Methods like reflow soldering or wave soldering are used depending on the design and scale of production.
Proper soldering ensures strong electrical connectionswhich is critical to the performance of the device. EMS companies take special care to automate this process for accuracy and reliability.
6. Testing and Quality Control
Before any electronic device can be shippedit undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets the necessary performance standards. Various testing methods are employedsuch as functional testingburn-in testingand automated optical inspection (AOI).
Testing ensures that the product performs as expected and that there are no defects in the circuitry or assembly. Electronic manufacturing services companies adhere to industry regulations and quality standardssuch as ISO certificationsto guarantee that products are safe and reliable.
7. Final Assembly and Packaging
In the final stagethe components are assembled into the final product housingand the device is packaged for distribution. This step involves attaching external componentssuch as screensbuttonsor casingand ensuring everything is securely in place.
Packaging must also be designed to protect the device during shipping. Efficient ERP systems play a vital role herecoordinating assembly and packaging to meet production deadlines while maintaining quality.
Each of these stages is crucial to the success of the electronic manufacturing industryand electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies have mastered these processes through automationtestingand ERP for manufacturing integration.
By streamlining each phasethese companies can deliver high-quality products at scalemeeting the growing demands of the global market.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques in Electronic Manufacturing
In addition to the key stages of the electronic manufacturing processmodern electronic manufacturing companies employ several advanced techniques to improve efficiencyaccuracyand scalability.
These techniques are essential for keeping up with the ever-evolving demands of the electronic manufacturing industry and ensuring that products meet high-quality standards.
1. Automation and Robotics
Automation has revolutionized electronic manufacturing services by reducing the need for manual labor in repetitive taskssuch as component placement and soldering.
Advanced robotics systems can handle intricate assembly processes with greater precision and speed than human workersminimizing errors and reducing production time.
Many electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies utilize automated solutions to streamline their operationsimprove yield ratesand reduce costs.
2. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a technique widely used in electronic design and manufacturing that allows components to be mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs without the need for pre-drilled holes.
SMT enables higher component density and faster assemblymaking it a preferred method for producing compacthigh-performance devices like smartphones and laptops.
This technology is vital for electronic manufacturing services companies aiming to increase production efficiency while maintaining quality.
3. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturingalso known as 3D printingis gaining traction in the electronic manufacturing industry for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
It allows for the creation of highly complex and customized components at a lower cost and with faster turnaround times. In addition to prototypes3D printing can be used to produce specialized parts that may be difficult or expensive to source through traditional methodsmaking it a valuable tool for electronic manufacturing companies.
4. Clean Room Manufacturing
Many electronic manufacturing services require the use of clean roomsparticularly in the production of sensitive components like semiconductors and medical devices.
Clean rooms maintain controlled environments with minimal dustcontaminantsand electrostatic discharge (ESD)which can damage delicate electronics. These environments are critical for ensuring that products meet stringent safety and quality standardsparticularly in industries like aerospacehealthcareand defense.
5. Lean Manufacturing and Just-in-Time (JIT) Production
To optimize efficiency and minimize wasteelectronic manufacturing companies often implement lean manufacturing principles and Just-in-Time (JIT) production strategies. These methods focus on reducing excess inventorystreamlining workflowsand delivering products precisely when needed.
With the help of ERP systems for manufacturingcompanies can closely monitor production schedules and supply chainsensuring that resources are used efficiently while maintaining product quality.
These additional techniques are pivotal to staying competitive in the electronic manufacturing industry. By leveraging advanced methods such as automationSMTand 3D printingelectronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies can achieve higher production efficiencydeliver more innovative productsand maintain the rigorous standards expected in today’s tech-driven market.
Supply Chain Management in Electronic Manufacturing
Effective supply chain management is critical in the electronic manufacturing industrywhere coordination between suppliersmanufacturersand distributors must be seamless.
From sourcing materials to delivering the final producteach link in the supply chain plays a vital role in ensuring timely production and maintaining high-quality standards.
Electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies rely heavily on optimized supply chain management to navigate complex global networks and respond to rapidly changing demands.
1. Material Sourcing and Procurement
One of the key components of supply chain management in electronic manufacturing is the sourcing of raw materials and electronic components. Manufacturers must secure reliable suppliers for critical materialssuch as semiconductorscapacitorsresistorsand metals.
Any disruption in this supply chain can lead to production delays. Electronic manufacturing companies use advanced ERP systems for manufacturing to manage supplier relationshipsmonitor inventory levelsand automate procurement processesensuring materials are available when needed.
2. Inventory Management
Inventory management is a balancing act in electronic manufacturing services. Having too much stock can lead to high holding costswhile too little can result in production bottlenecks.
Manufacturing ERP solutions provide real-time visibility into inventory levelsallowing electronic manufacturing companies to implement Just-in-Time (JIT) strategies.
This approach minimizes excess inventoryreduces wasteand ensures that components are available right when they are neededimproving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
3. Logistics and Distribution
Once the product is manufacturedit must be delivered to customers or distributors in a timely and efficient manner. Coordinating global logisticsespecially for large-scale electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companiescan be challenging due to varying customs regulationstransportation costsand delivery timelines.
Electronic manufacturing companies often leverage ERP systems to track shipmentsmanage international logisticsand ensure smooth transitions from factory to customer.
4. Risk Management and Supplier Diversification
In the electronic manufacturing industrysupply chain disruptions can have a significant impact on production timelines and costs. Natural disasterspolitical instabilityor supply shortages can all create risks for manufacturers.
To mitigate these riskselectronic manufacturing companies employ strategies such as supplier diversification—working with multiple suppliers for critical components to avoid relying too heavily on one source.
Advanced ERP for manufacturing systems provide analytics and forecasting tools to help companies anticipate disruptions and adjust accordingly.
5. Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
As sustainability becomes a greater focus for the electronic manufacturing industrycompanies are under increasing pressure to ensure that their supply chains adhere to environmentally responsible practices. This includes ethical sourcing of materials like rare earth metals and ensuring that suppliers comply with environmental regulations.
Electronic manufacturing services companies are also exploring sustainable packaging and energy-efficient logistics to reduce their carbon footprint. Modern ERP systems for manufacturing help companies track and report on sustainability metricsensuring that they meet industry and regulatory standards.
By implementing robust supply chain management strategieselectronic manufacturing companies can better navigate the complexities of global productionoptimize their workflowsand respond quickly to shifts in demand.
The integration of ERP systems enhances visibilityefficiencyand coordination across the supply chainallowing electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies to deliver high-quality products on time while managing costs and risks effectively.
Challenges and Risks in Electronic Manufacturing and How to Overcome Them
The electronic manufacturing industry faces a unique set of challenges and risks due to the complexity and scale of production. These obstaclesranging from supply chain disruptions to technological advancementscan hinder operations and affect profitability.
Howeverwith the right strategieselectronic manufacturing companies can mitigate these risks and maintain smooth operations. Below are some common challenges faced by electronic manufacturing services and solutions to combat them.
1. Supply Chain Disruptions
One of the most significant risks in electronic manufacturing is supply chain disruption. Components such as semiconductorsmetalsand other critical materials may face shortagesdelayed deliveriesor price fluctuationswhich can stall production timelines. This risk has been heightened in recent years due to global events like pandemics and trade disputes.
Solution: To overcome this challengeelectronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies can adopt ERP systems for manufacturing that include predictive analytics and demand forecasting. These systems allow companies to anticipate potential shortages and source alternative suppliersdiversifying the supply chain to reduce dependency on a single source.
Advanced ERP solutions can also automate inventory managementhelping businesses implement Just-in-Time (JIT) strategies to reduce excess stock and manage costs more effectively.
2. Rapid Technological Advancements
The electronic manufacturing industry is constantly evolving due to technological advancements. Keeping up with new technologiesproduction techniquesand consumer demands can be a challengeespecially for smaller electronic manufacturing services companies.
Solution: Investing in Manufacturing ERP systems that are designed to scale and adapt to technological changes is essential. ERP systems can integrate new production tools and methodologies quicklyallowing electronic manufacturing companies to stay competitive. Additionallyregular employee training on the latest technologies and trends can help teams adapt faster to new production requirements.
3. Quality Control and Product Defects
Ensuring that all products meet high-quality standards is a significant challenge in electronic manufacturing. Defects in electronic devices can lead to expensive recallsdamage to brand reputationand customer dissatisfaction. Maintaining strict quality control during productionfrom design to final testingis essential.
Solution: To combat quality issueselectronic manufacturing services companies can implement automated testing processessuch as automated optical inspection (AOI) and functional testing.
Additionallyintegrating real-time data monitoring through ERP systems for manufacturing can allow for early detection of defectsreducing waste and ensuring that faulty products do not reach the market.
Lean manufacturing techniques can also be employed to minimize waste and ensure that quality is built into every step of the production process.
4. Cost Pressures
Manufacturers constantly face pressure to reduce costs while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency. Fluctuating material costsrising labor expensesand the need to invest in advanced technologies can strain budgets and affect profitability for electronic manufacturing companies.
Solution: Implementing cost-effective automation solutions and utilizing ERP for manufacturing can help streamline operations and reduce manual labor costs. Lean manufacturing practices can also reduce wasteoptimize resource useand improve overall efficiency.
Moreoverelectronic manufacturing companies can leverage ERP systems to manage and forecast costsensuring that they remain competitive without sacrificing product quality.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental regulationsproduct safety standardsand labor laws is a critical challenge for electronic manufacturing services companies. The industry is subject to numerous regulatory frameworkswhich vary by region and can be complex to navigate. Failing to meet these requirements can result in penaltieslegal issuesor the inability to sell products in certain markets.
Solution: ERP systems with built-in compliance management tools can help companies stay updated with the latest regulations and ensure that all products meet the necessary standards.
These systems can track compliance across the supply chainensuring that all components and processes adhere to relevant environmentalsafetyand labor regulations.
By addressing these challenges with modern solutionselectronic manufacturing companies can remain resilient and competitive in a fast-paced industry.
Leveraging tools like manufacturing ERP and embracing automation not only mitigates risks but also enhances operational efficiencyallowing businesses to deliver high-quality products while staying agile in the face of change.
Compliance and Standards in Electronic Manufacturing
Compliance with industry standards and regulatory frameworks is essential for electronic manufacturing companies to ensure product safetyenvironmental responsibilityand market access.
The electronic manufacturing industry is governed by a wide range of regulations that vary across regionscovering everything from product quality to environmental impact.
Non-compliance can lead to significant financial penaltieslegal complicationsand damage to a company’s reputationmaking it critical for electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies to prioritize adherence to these standards.
1. Environmental Compliance
Environmental sustainability is a growing focus in the electronic manufacturing industrywith companies required to meet strict environmental regulations to minimize their ecological footprint.
Two of the most widely recognized environmental standards are the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directivesparticularly enforced in the European Union.
These regulations govern the use of hazardous materials like lead and mercury in electronic devices and dictate the proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste.
Solution: Electronic manufacturing services companies can achieve compliance by integrating ERP for manufacturing systems that track and manage materials used in production.
These systems help manufacturers ensure that they source components that meet RoHS and WEEE standardsand allow for detailed reporting on compliance with environmental regulations.
Adopting sustainable manufacturing practicessuch as reducing emissions and using eco-friendly packagingalso supports compliance efforts.
2. Product Safety and Quality Standards
To ensure that electronic products are safe for consumer useelectronic manufacturing companies must adhere to product safety standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certifications.
ISO 9001 establishes the criteria for a quality management systemensuring that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. UL certification verifies that a product has been tested and meets safety standards for electrical devices.
Solution: To maintain product safety and qualityelectronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies can implement stringent quality control systemsoften facilitated by manufacturing ERP solutions. These systems help monitor production processestest componentsand identify potential defects before products leave the factory.
Additionallyautomated testing proceduressuch as AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) and functional testingensure that all products comply with the relevant safety standards.
3. International Trade Compliance
For electronic manufacturing companies that operate globallynavigating international trade regulations is a critical aspect of compliance. This includes adhering to export control lawsimport tariffsand customs requirements.
Companies must also ensure compliance with international standardssuch as the CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area and the FCC regulations for electronics sold in the United States.
Solution: Advanced ERP systems can help electronic manufacturing services companies manage the complexities of international trade compliance by automating customs documentationmonitoring tariffsand ensuring adherence to local market standards.
These systems can also track the country of origin for componentshelping companies ensure that they comply with trade agreements and avoid penalties.
4. Labor and Ethical Standards
In addition to product and environmental standardselectronic manufacturing companies must comply with labor laws and ethical sourcing guidelines.
This includes ensuring safe working conditionsfair wagesand compliance with regulations such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and International Labour Organization (ILO) conventions.
Many global companies also commit to avoiding conflict minerals—materials sourced from conflict zones where mining may fund violence and exploitation.
Solution: Compliance with labor and ethical standards can be achieved through ERP systems for manufacturingwhich help companies monitor supplier practicestrack labor conditionsand ensure ethical sourcing of materials.
By maintaining transparency throughout the supply chainelectronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies can demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices and meet the growing demand for ethically produced electronics.
Maintaining compliance with these critical standards and regulations is essential for electronic manufacturing companies to stay competitiveavoid penaltiesand uphold their reputations.
By leveraging ERP systems and implementing rigorous monitoring and reporting processescompanies can ensure that their products meet all necessary requirementsboth domestically and internationally.
Future Trends in Electronic Manufacturing
The electronic manufacturing industry is evolving rapidlydriven by advancements in technologychanging consumer demandsand a growing emphasis on sustainability.
Electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies are now adapting to trends that will reshape how electronics are designedproducedand delivered. Below are some of the key trends shaping the future of electronic manufacturing.
1. Increased Automation and Robotics
Automation has been a key driver of efficiency in electronic manufacturingand this trend is expected to continue growing. Advanced roboticsmachine learningand artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly being integrated into production lines to improve precisionreduce human errorand optimize workflows. Electronic manufacturing companies are investing in smart factorieswhere machines communicate with each other to perform tasks more efficiently.
Impact: Automation reduces production costsincreases the speed of manufacturingand enhances quality control.
For electronic manufacturing services companiesembracing automation will be critical to staying competitiveespecially in high-demand industries like consumer electronics and automotive manufacturing.
Manufacturing ERP systems will play a central role in managing these automated processesensuring seamless coordination between human workers and machines.
2. Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming not only the products being manufactured but also the manufacturing process itself. IoT-enabled devices collect real-time data from production linesenabling manufacturers to monitor equipment performancepredict maintenance needsand reduce downtime. AdditionallyIoT technology is being used to improve supply chain visibility by tracking components from supplier to final product.
Impact: IoT helps electronic manufacturing companies enhance operational efficiencyreduce wasteand optimize energy use. Electronic manufacturing services will benefit from the integration of IoT technologies into ERP systemswhich can process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices to improve decision-making.
3. Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the electronic manufacturing industry as consumers and regulators push for more environmentally responsible practices.
Reducing carbon footprintsminimizing electronic wasteand improving energy efficiency are all key concerns for electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies. As a resultmanufacturers are exploring sustainable materialsgreen energy sourcesand eco-friendly production processes.
Impact: Companies that prioritize sustainability will gain a competitive advantage by meeting consumer demand for greener products and complying with stricter environmental regulations.
Manufacturing ERP systems can help track sustainability metricsmanage energy useand ensure compliance with environmental standardssuch as RoHS and WEEE.
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturingor 3D printingis poised to revolutionize the electronic manufacturing process by enabling rapid prototyping and small-scale production. This technology allows manufacturers to create complex electronic components with greater flexibility and speedreducing the need for traditionaltime-consuming manufacturing methods.
Impact: Additive manufacturing will enable electronic design and manufacturing companies to bring products to market faster and at a lower cost. It also supports greater customizationallowing manufacturers to produce small batches of specialized components without the expense of retooling traditional machinery.
5. Advanced Materials and Miniaturization
The demand for smallermore powerful electronic devices is driving innovation in materials and component design. Advances in nanotechnologyflexible electronicsand high-performance materials like graphene are enabling manufacturers to create smallerlighterand more energy-efficient devices. This trend is particularly important for industries such as wearable technologymedical devicesand telecommunications.
Impact: Electronic manufacturing services companies that can adopt these advanced materials will be better positioned to meet the demands of cutting-edge industries. ERP for manufacturing systems will play a crucial role in managing the complexities of producing and integrating these advanced materialsensuring high-quality production standards are maintained.
6. Globalization and Localized Manufacturing
While globalization has long been a defining characteristic of electronic manufacturingthere is a growing shift toward localized manufacturing. This trend is being driven by the need for faster time-to-marketsupply chain resilienceand customization for local markets. Localized manufacturing allows companies to reduce lead timeslower transportation costsand address regional regulatory requirements more easily.
Impact: Electronic manufacturing companies that invest in localized production facilities will benefit from greater agility and the ability to respond more quickly to changing consumer demands. ERP systems for manufacturing will be essential for coordinating global and local operationsensuring consistency and compliance across different markets.
By embracing these future trendselectronic manufacturing services companies can stay at the forefront of the industrydriving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
The integration of ERP systems and emerging technologies will be crucial in managing the complexities of these trendsensuring efficiencysustainabilityand agility in an increasingly dynamic market.
How AI Enhances Manufacturing Processes
AI algorithms analyze real-time data to optimize production workflowsreduce machine downtime through predictive maintenanceand ensure quality control by detecting defects early.
AI also helps manufacturers manage inventory more accuratelyforecast demandand automate routine tasksallowing teams to focus on innovation and strategy.
By unifying data and streamlining operations across departmentsAI not only enhances productivity but also enables faster decision-making and cost savings.
How Deskera ERP and MRP Can Enhance Electronic Manufacturing ?
In the rapidly evolving electronic manufacturing industryefficiencyprecisionand real-time data are critical to success.
Deskera ERP and Deskera MRP offer powerful solutions to help electronic manufacturing companies streamline their operationsoptimize productionand maintain compliance with industry standards.
By integrating ERP and MRP systems into their processesmanufacturers can achieve greater visibility and control over every stage of production.
1. Streamlined Inventory Management
One of the most significant challenges in electronic manufacturing is managing complex inventories with numerous components and materials. Deskera ERP provides real-time tracking of inventory levelsensuring that manufacturers have the parts they need when they need them. This prevents production delays due to stockouts and minimizes excess inventoryreducing overall costs.
AdditionallyDeskera MRP helps manufacturers plan their material requirements more effectivelyensuring that the right materials are ordered at the right time. This is particularly crucial for electronic manufacturing services (EMS) companies that must balance high demand with tight production schedules.
2. Production Planning and Scheduling
Efficient production planning is key to staying competitive in the electronic manufacturing industry. Deskera MRP helps companies optimize their production schedules by analyzing demand forecastsmaterial availabilityand labor capacity. This ensures that production runs smoothlywith minimal disruptions or downtime.
With Deskera ERPmanufacturers can track production progress in real-timeenabling them to make quick adjustments if issues arise. This level of control is essential for electronic manufacturing services companies that need to meet tight deadlines and deliver high-quality products on time.
3. Compliance and Quality Control
Adhering to strict industry regulations and maintaining high product quality are critical for electronic manufacturing companies. Deskera ERP allows manufacturers to track every step of the production processensuring that products meet regulatory requirements and quality standards.
Deskera MRP can be used to schedule routine quality checks and automate testing proceduresto catch any defects early. This helps reduce wasteimprove product reliabilityand ensure compliance with standards like ISO 9001RoHSand WEEE.
4. Improved Supply Chain Management
Managing suppliers and logistics is a complex task in electronic manufacturing. Deskera ERP offers integrated supply chain management featuresallowing manufacturers to track shipmentsmanage supplier relationshipsand ensure timely delivery of materials. With real-time visibility into the supply chainmanufacturers can reduce lead times and avoid disruptions that can affect production.
By leveraging Deskera ERP and MRPelectronic manufacturing services companies can also maintain better collaboration with suppliersensuring they receive high-quality components and materials while minimizing costs.
5. Cost Control and Financial Management
Managing costs is crucial for profitability in the highly competitive electronic manufacturing industry. Deskera ERP helps companies gain a clear view of their financialstracking expensesrevenueand profitability across all operations. With real-time financial datamanufacturers can make informed decisions to reduce costs and improve margins.
By automating routine financial taskssuch as invoicing and payrollDeskera ERP also reduces the risk of errors and frees up valuable time for financial teams to focus on strategic planning.
Deskera ERP and MRP provide electronic manufacturing companies with the tools they need to stay competitivemaintain product qualityand streamline operations. From inventory management and production planning to compliance and financial controlDeskera’s solutions help manufacturers thrive in a fast-paceddynamic industry.
Key Takeaways
- The electronic manufacturing process encompasses various stagesfrom design and prototyping to production and assemblymaking it crucial for developing reliable and innovative electronic products.
- Electronic manufacturing involves the production of electronic components and assembliesplaying a pivotal role in various industriesincluding consumer electronicsautomotiveand telecommunications.
- Understanding the key stages of electronic manufacturing—designprototypingproductionassemblyand testing—is essential for ensuring product quality and meeting market demands.
- Incorporating advanced manufacturing techniques such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT)Through-Hole Technologyand Additive Manufacturing can enhance efficiency and flexibility in electronic manufacturing.
- Effective supply chain management is critical for electronic manufacturers to ensure timely delivery of componentsminimize disruptionsand maintain product quality.
- The electronic manufacturing industry faces challenges such as supply chain disruptionstechnological changesand regulatory compliance; proactive strategies are essential for mitigating these risks.
- Adhering to industry standards and regulations (like ISORoHSand WEEE) is vital for ensuring product safetyqualityand environmental responsibility in electronic manufacturing.
- The future of electronic manufacturing is characterized by increased automationthe rise of IoTsustainable practicesand the adoption of advanced materialsdriving innovation and efficiency.
- Deskera ERP and MRP provide essential tools for electronic manufacturers to streamline operationsoptimize inventory managementand improve production planningensuring competitiveness in the industry.
Related Articles