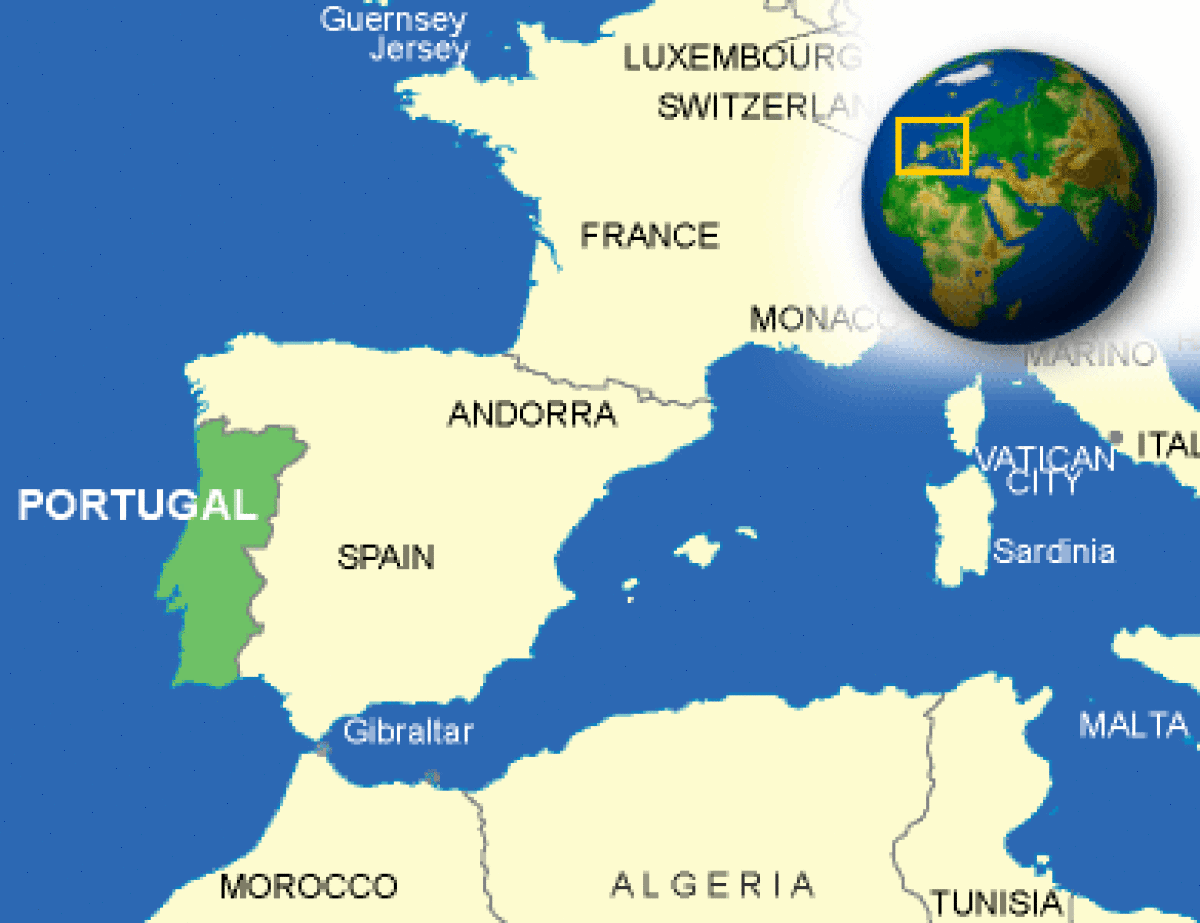
Where is Portugal located?
What countries border Portugal?
Portugal Weather
What is the current weather in Portugal?
Portugal Facts and Culture
What is Portugal famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Portuguese are generally conservative and traditional. Howeverthey are very open and friendly to people of other nations. ... More
- Family: The family is the core of Portuguese life. Nuclear families tend to be minoraveraging two children. Women often... More
- Personal Apperance: The Portuguese are usually conservative in their dress. Men typically wear a suit to work. Clothing is usually well-keptand... More
- Recreation: Football (soccer) is the most popular sport. Golf and tennis are also widely played. Watching bullfights and dancing are popular... More
- Diet: Portugal's staple foods include fishvegetablesand fruits. One of the national dishes is bacalhau (dried cod)which is usually... More
- Food and Recipes: Portuguese eat according to the continental . They use a knife and fork. They should not stretch at the table,... More
- Visiting: When visitingone waits outside until invited in by the host. It is expected that a guest wipes their... More
- Dating: Dating habits in Portugal are similar to those currently prevailing in the rest of Europealthough they are more conservative... More
Portugal Facts
What is the capital of Portugal?
| Capital | Lisbon |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
35,556 Square Miles 92,090 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southwestern Europebordering the North Atlantic Oceanwest of Spain |
| Language | Portuguese (official)Mirandese (official - but locally used) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $27,800.00 (USD) |
Portugal Demographics
What is the population of Portugal?
| Ethnic Groups | Portuguese 95%; citizens from Portugal’s former colonies in AfricaAsia (Han Chinese)and South America (Brazilian) and other foreign born 5% |
| Languages | Portuguese (official)Mirandese (officialbut locally used) |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Portuguese (singular and plural) adjective: Portuguese |
| Population | 10,207,177 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.14% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 3.001 million LISBON (capital)1.325 million Porto |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 67.9% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.44% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 4,835,763 female: 5,371,414 |
Portugal Government
What type of government does Portugal have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Marcelo REBELO DE SOUSA (since 9 March 2016) head of government: Prime Minister Antonio Luis MONTENEGRO (since 2 April 2024) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 roundsif neededfor a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); following legislative electionsthe president usually appoints the leader of the majority party or majority coalition as prime minister most recent election date: 24 January 2021 election results: 2021: Marcelo REBELO DE SOUSA reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Marcelo REBELO DE SOUSA (PSD) 60.7%Ana GOMES (ran as an independent but is a member of PS) 13%Andre VENTURA (CH) 11.9%João FERREIRA (PCP-PEV) 4.3%other 10.1% 2016: Marcelo REBELO DE SOUSA elected president in the first round; percent of vote - Marcelo REBELO DE SOUSA (PSD) 52%António SAMPAIO DA NOVOA (independent) 22.9%Marisa MATIAS (BE) 10.1%Maria DE BELEM ROSEIRA (PS) 4.2%other 10.8% expected date of next election: January 2026 note: there is also a Council of State that acts as a consultative body to the president |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Portugal dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years; 6 years if from a Portuguese-speaking country |
| National Holiday | Portugal Day (Dia de Portugal)10 June (1580); note - also called Camoes Daythe day that revered national poet Luis DE CAMOES (1524-80) died |
| Constitution | proposed by the Assembly of the Republic; adoption requires two-thirds majority vote of Assembly members; amended several timeslast in 2005 |
| Independence | 1143 (Kingdom of Portugal recognized); 1 December 1640 (independence reestablished following 60 years of Spanish rule); 5 October 1910 (republic proclaimed) |
Portugal Video
YouTubeExpoza Travel Portugal Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Portugal Geography
What environmental issues does Portugal have?
| Overview |
Portugalin Europe’s southwest corneris part of the Iberian Peninsula. The country is made up of the mainland and the Azores and Madeira Islands. On the north and eastPortugal is bordered by Spain; on the south and west by the Atlantic Ocean. The Tagus Riverflowing west into the Atlantic at Lisbon divides mainland Portugal into two distinct topographical and climatic regions. The northern part of the country is mountainous. Its climate is relatively cool and rainy. In the south there are lowrolling plains. The climate is drier and warmerparticularly in the interior. Lying about 800 miles west of Lisbon in the Atlantic Oceanthe Azores are a chain of nine mountainous islands of volcanic origin. Their climate tends to be moist and moderate throughout the year. The total land area of the nine islands is 888 sq. miles. The two main islands and the numerous smalleruninhabited islands that make up the Madeira chain are located in the Atlantic Ocean about 350 miles west of Morocco. The islands are mountainous and ruggedwith a mild year-round climate. Total land area is slightly over 300 sq. miles. |
| Climate |
Mainland Portugal experiences two distinct seasons. From late October to mid-May rain is frequent and sometimes heavy. Temperatures may drop into the low 30s at night during the coldest monthswith daytime highs in the 50s and 60s. Annual variations in rainfall can be considerablewith years of flooding followed by years of drought. The remainder of the year is normally sunny with minimal rainfall. Days are pleasantwith temperatures seldom exceeding 95° Fexcept in the southern interior of the country. Afternoons and evenings are breezywith nighttime temperatures in the 60s and low 70s. Spells of intense heat are infrequent and last only a few days. The Tagus Riverflowing west into the Atlantic at Lisbon divides mainland Portugal into two distinct climatic regions. The northern part is relatively cool and rainy. In the south the climate is drier and warmerparticularly in the interior. The Azores climate tends to be moist and moderate throughout the year. |
| Border Countries | Spain 1,214 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | soil erosion; air pollution caused by industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollutionespecially in coastal areas |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air PollutionBiodiversityClimate ChangeClimate Change-Kyoto ProtocolDesertificationEndangered SpeciesHazardous WastesLaw of the SeaMarine DumpingMarine Life ConservationOzone Layer ProtectionShip PollutionTropical Timber 83Tropical Timber 94WetlandsWhaling signedbut not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic PollutantsAir Pollution-Volatile Organic CompoundsEnvironmental Modification |
| Terrain | mountainous north of the Tagus Riverrolling plains in south |
Portugal Economy
How big is the Portugal economy?
| Economic Overview |
Portugal's economic history is deeply intertwined with its colonial pastmaritime prowessand periods of economic hardship. During the Age of Discoveryduring the 15th and 16th centuriesPortugal established a vast overseas empireenriching the nation through trade in spicesgoldand other commodities. Howeverthe decline of its empire and the devastating earthquake of 1755 ushered in a period of economic stagnation. Modern Economic Evolution: In the 20th centuryPortugal underwent significant economic transformations. Joining the European Union in 1986 paved the way for economic integration and development. The country embraced structural reformsprivatizationand investments in infrastructureleading to robust economic growth during the 1990s and early 2000s. HoweverPortugal faced challenges such as high public debtlow productivityand unemploymentexacerbated by the global financial crisis 2008. Post-Crisis Recovery: In response to the crisisPortugal implemented austerity measures and pursued fiscal consolidationalbeit with social costs. The country underwent structural reforms in labor marketspensionsand the financial sectorsupported by external financial assistance from the EU and IMF. Despite initial hardshipsPortugal's economy reboundedwith improved competitivenessexport growthand a gradual decline in unemployment. Current Economic Landscape: According to the latest dataPortugal's economy continues to show resilience amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The government's swift responseincluding fiscal stimulus measures and support for businesseshelped cushion the crisis's impact. HoweverPortugal faces persistent structural issuesincluding an aging populationlow productivity growthand regional disparities. Key Economic Indicators: GDP Growth: Portugal's GDP growth has shown recoveryalbeit at a moderate pace. In recent yearsgrowth rates have hovered around 2%driven by domestic consumptionexportsand tourism. Unemployment: While decliningunemployment rates remain above the EU average. Efforts to address youth unemployment and skills mismatches are ongoing. Public Debt: Portugal's public debtthough highhas gradually decreased from its peak. Continued fiscal discipline and debt sustainability are priorities for the government. External Trade: Portugal maintains a positive trade balancewith exports accounting for a significant portion of GDP. Key export sectors include automotivetextilesand agro-food products. |
| Industries | textiles and footwear; wood pulppaperand cork; metalworking; oil refining; chemicals; fish canning; wine; tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Spain 20.3%Germany 18.4%France 12.6%UK 10.5%US 5.8%Italy 4.8%Belgium 4.5% |
| Import Partners | Spain 28.1%Germany 15%France 10.2%Italy 6.5%UK 5.2%Netherlands 4.5% |
Portugal News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Portugal?
Source: Google News
Portugal Travel Information
What makes Portugal a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Portugal is a developed and stable democracy with a developed economy. Tourist facilities are widely available.
Crime
Portugal has a relatively low rate of violent crime; howevercrime in all categories is steadily increasing. Your greatest crime risk is becoming a target of pickpockets and purse snatchersparticularly at popular tourist sites and restaurantsor on public transportation. Rental cars and vehicles with out-of-town or foreign license plates are frequent targets for break-insparticularly when parked in popular tourist destinations and beaches. You should always remove visible luggage or personal items from cars when parking. The Embassy has learned of incidents where travelers discover a flat tire and someone immediately volunteers to assist. Capitalizing on the distractionan accomplice meanwhile steals valuables from the vehicle. Keep your car doors locked when stopped at intersections. You should also avoid using automatic teller machines (ATMs) in isolated or poorly lighted areas. In generalvisitors to Portugal should carry limited cash and credit cards on their personand leave extra cashcredit cardsand personal documents at home or in a hotel safe. While thieves may operate anywherethe U.S. Embassy receives most reports of theft from the following areas:Lisbon: Pick pocketing and purse snatchings in the Lisbon area are most likely to occur in buseshotel lobbiesrestaurantsthe airporttrainstrain stationsand tramsespecially onboard tram number 28 to the Castle of São Jorge. At restaurantsitems that hang over the backs of chairs or are placed on the floor are particularly vulnerable. Unattended luggage can be stolen at the Lisbon Airport. You should take special care in the OrienteSanta Apoloniaand Rossio train stationsthe Sete Rios bus stationthe AlfamaBaixa and Bairro Alto districtsand the tourist area of Belém.
Outside Lisbon: Thefts have been reported in the popular tourist destination towns of SintraCascaisMafraFatimaand in the Algarve. Thieves reportedly scout parking areas alongside tourist attractions and beaches watching for rented cars. You should take special care when parking at the Moorish Castle and Pena Palace in Sintra; and at the beachfront areas of GuinchoCabo da Rocaand Boca do Inferno. We have received some reports that vacation homes have been robbed in the Algarve. When renting vacation lodgingmake sure to assess the accommodation’s security systems.
Madeira: Pick pocketingwhile infrequentmay occur in the Old Town and Santa Catarina Park areas of Funchal.
Trains: Public transportation is considered safe and reliable; howeverduring the summer monthsthere are occasionally reports of youth gangs accosting passengers riding trains between LisbonCascaisand Sintra. The authorities have increased their patrols in response to these incidents.
Taxis: Taxis are a reliable means of transportationthough you should be alert to possible discrepancies between the meter fare and the amount requested by the driver. Always ask the taxi driver to use the meter. A tourism information kiosk in the arrivals area of the Lisbon airport sells taxi vouchers at standardized prices for many locations in the city and metro area. As part of this voucher servicea member of the tourism office will also escort you to your taxi. Some cases have been reported involving taxi drivers in the arrivals area of the airport who overchargethreaten and/or harass passengers.
Beaches: Beaches are generally considered safebut beachgoers should not leave their personal belongings unattended. Youth gangs have been known to congregate along the beaches between Lisbon and Cascais and occasionally accost beach-goers. The authorities have increased their patrols in response to these incidences.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goodseven if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United Statesif you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Portugalyou are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own..Although it is not illegalit is advisable not to take pictures of military and security sites in Portugal. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy bootleg or pirated goods.Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Portugalyour U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.
Possession and use of narcotic drugs is an administrative offense in Portugaland users can face mandatory drug treatment. Penalties for trafficking in illegal drugs are severeand offenders can expect long jail sentences.
Arrest notifications in host country: While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign countrythat might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstancesrequest that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Languages
Portuguese (official)Mirandese (officialbut locally used)
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Good medical care is availablebut facilities may be limited outside urban areas. Public hospitals offer services at costs lower than private hospitalsbut sometimes do not maintain the same comforts as hospitals in the United States. You should obtain insurance that covers medical services from a private Portuguese hospital or clinic. Private hospitals will ask for a credit card or other form of payment upon admission. In a life-threatening emergencyyou can ask for a public ambulance by calling the national emergency response telephone number112. On the other handprivate ambulances should only be used for transportnot life-threatening emergenciesand usually require on-the-spot payment. Note that the responsiveness of emergency services is not up to U.S. standards.Prescription Medicines: Travelers sometimes request that relatives or friends in the United States mail prescription medicines to them in Portugalbut doing so violates Portuguese law and usually results in the shipment of medications being impounded by the Portuguese customs office. When this occursyour medications may not be released. If you use prescription medicineyou must bring a sufficient supply with you to cover your anticipated stay in Portugalalong with a copy of your physician's prescription. Should an unforeseen need for prescription refills or new medications arisePortuguese pharmacies generally carry equivalent medications to those found in the United States; howeverthey may be sold under a different brandmay not be available in the same dosageand may require a prescription from a local doctor.
Safety and Security
Portugal remains largely free of terrorist incidents; howeverlike other countries in the Schengen areaPortugal’s open borders with its Western European neighbors allow possible terrorist groups to enter and exit the country with anonymity. U.S. citizens are reminded to remain vigilant with regard to their personal security.General strikes and public protests against government austerity measures have occurred with increased frequency during 2012. These are rarely violentbut travelers are advised to avoid areas where these public protests are taking place.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Portugalyou may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.While Portugal has significantly expanded its motorway network with well-constructed roadsleading to a resulting decrease in accidents and fatalitiesits road-accident fatality rate is still higher than the EU averageaccording to Eurostat. You should use cautionas aggressive driving habits and high speeds pose special hazards. Use appropriate care and caution while on the roadwayspractice safe driving habitsand adhere to the applicable speed limits.
Fines for traffic offenses are substantial in Portugal. Speedingdriving under the influence of alcohol or drugsand the use of mobile phones while driving are heavily penalized. Use of seatbelts is mandatory for drivers and passengers. Small children must be in child safety seats with the seatbelts fastened in the back of your car. The police in continental Portugal have the authority to fine on-the-spot and most of their vehicles have portable ATM machines to facilitate immediate payment.
Taxis are a reliable means of transportationbut are subject to the same road conditions listed above. Refer to the crime section of this page to alert yourself to other threats relating to taxis.
Buses are reliable.
In the Azoresdriving can be challenging due to narrow cobblestone streetsblind curvesblind cornersand herds of cows on country roads. In contrast to the situation on the Portuguese mainlandpayments are not made on the spot; traffic violations are registered by radar and later forwarded to the offender via the postal service. Taxis do not have meters; the fare consists of a base fee plus a posted rate per kilometer traveled. Public buses are inexpensive. Bus services begin at 7 a.m. and generally operate until 8 p.m.depending on the destination.
U.S. citizen visitors to Portugal may drive with a valid U.S. driver's license for up to six months. For international driving permitsplease contact AAA or the National Auto Club.
